A Data-Independent-Acquisition-based proteomic approach towards understanding the acclimation strategy of Microchloropsis gaditana CCMP526 in hypersaline conditions
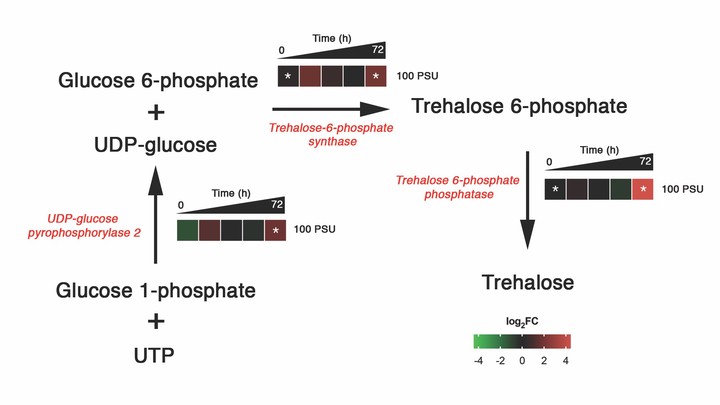 Salinity induced temporal dynamics of proteins involved in trehalose biosynthesis in M. gaditana.
Salinity induced temporal dynamics of proteins involved in trehalose biosynthesis in M. gaditana.
Abstract
Salinity is one of the significant factors that affect growth and cellular metabolism, including photosynthesis and lipid accumulation, in microalgae and higher plants. Microchloropsis gaditana CCMP526 can acclimatize to different salinity levels by accumulating compatible solutes, carbohydrates, and lipids as an energy storage molecule. We used proteomics to understand the molecular basis for acclimation of M. gaditana to increased salinity levels (55 and 100 PSU (Practical Salinity Unit). Correspondence analysis (CA) was used for the identification of salinity-responsive proteins (SRPs). The highest number of altered proteins was observed in 100 PSU. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis revealed a separate path of acclimation for cells exposed to 55 and 100 PSU. Osmolyte and lipid biosynthesis was up-regulated in high saline conditions. However, concomitantly lipid oxidation pathways were also up-regulated at high saline conditions, providing acetyl-CoA for energy metabolism through the TCA cycle. Carbon fixation and photosynthesis were tightly regulated, while chlorophyll biosynthesis was affected under high salinity conditions. Importantly, temporal proteome analysis of salinity-challenged M. gaditana revealed vital salinity-responsive proteins which could be used for strain engineering for improved salinity resistance.