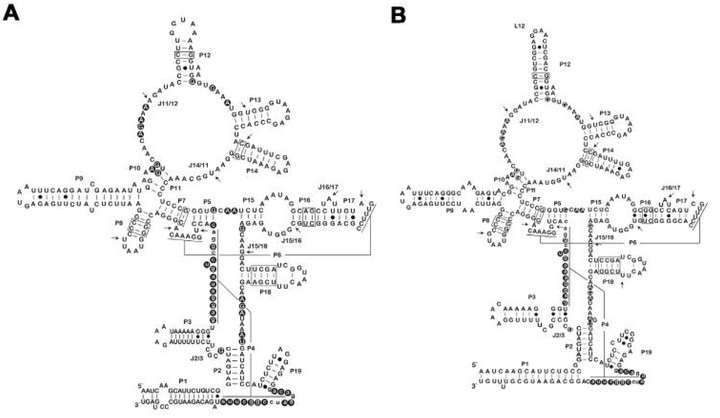
 Secondary and tertiary interactions between nucleotides of various domains present in RPRs of (A) Leptospira interrogans serovar Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni strain Fiocruz L (1e130) (pathogenic group I), (B) Leptospira kmetyi serovar Malaysia strain Bejo-Iso 9 (pathogenic group II)
Secondary and tertiary interactions between nucleotides of various domains present in RPRs of (A) Leptospira interrogans serovar Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni strain Fiocruz L (1e130) (pathogenic group I), (B) Leptospira kmetyi serovar Malaysia strain Bejo-Iso 9 (pathogenic group II)
We have employed the RNase P RNA (RPR) gene, which is present as single copy in chromosome I of Leptospira spp. to investigate the phylogeny of structural domains present in the RNA subunit of the tRNA processing enzyme, RNase P. RPR gene sequences of 150 strains derived from NCBI database along with sequences determined from 8 reference strains were examined to fathom strain specific structural differences present in leptospiral RPR. Sequence variations in the RPR gene impacted on the configuration of loops, stems and bulges found in the RPR highlighting species and strain specific structural motifs. In vitro transcribed leptospiral RPR ribozymes are demonstrated to process pre-tRNA into mature tRNA in consonance with the positioning of Leptospira in the taxonomic domain of bacteria. RPR sequence datasets used to construct a phylogenetic tree exemplified the segregation of strains into their respective lineages with a (re)speciation of strain SH 9 to Leptospira borgpetersenii, strains Fiocruz LV 3954 and Fiocruz LV 4135 to Leptospira santarosai, strain CBC 613 to Leptospira kirschneri and strain HAI 1536 to Leptospira noguchii. Furthermore, it allowed characterization of an isolate P2653, presumptively characterized as either serovar Hebdomadis, Kremastos or Longnan to Leptospira weilii, serovar Longnan.